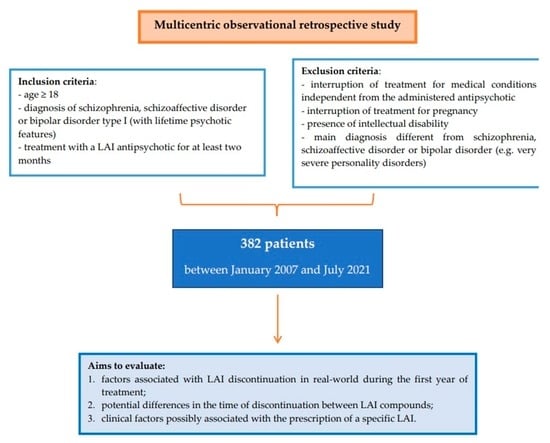
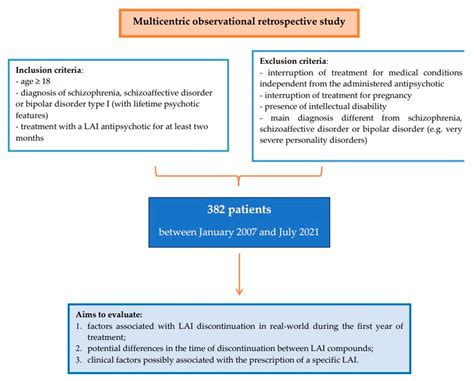
Schizoaffective disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by symptoms of both schizophrenia and mood disorders. This dual nature can significantly affect various aspects of an individual’s life, including career advancement and personal development. Understanding the nuances of this disorder is crucial for navigating the challenges it presents. In this article, we will explore the definition and symptoms of schizoaffective disorder, how it impacts career progression, and effective coping strategies. We will also discuss workplace accommodations, personal development, and self-care practices. Through success stories and a curated list of resources, we aim to provide valuable insights and support for those affected by schizoaffective disorder.
terylblog.com offers a detailed exploration of this topic.
1. Definition and Overview
Schizoaffective disorder is a chronic mental health condition that combines features of both schizophrenia and mood disorders, such as bipolar disorder or major depressive disorder. This disorder is characterized by the presence of psychotic symptoms—such as hallucinations or delusions—alongside significant mood disturbances. Unlike schizophrenia, which primarily involves psychotic symptoms, or mood disorders that focus on emotional disturbances, schizoaffective disorder encompasses elements of both, leading to a complex clinical picture.
The onset of schizoaffective disorder typically occurs in late adolescence or early adulthood, though symptoms can emerge at various stages of life. Diagnosis involves assessing the duration and severity of symptoms, which must include both psychotic and mood components for a significant portion of time. The condition can vary widely in its presentation, making it essential for individuals to receive a comprehensive evaluation from a mental health professional. Understanding schizoaffective disorder is crucial for managing its effects on daily life, including its impact on career and personal development.
2. Symptoms and Diagnosis
Schizoaffective disorder presents with a combination of symptoms from both schizophrenia and mood disorders. Key symptoms include psychotic features such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking, alongside mood disturbances like depression or manic episodes. These mood symptoms can vary, presenting as either intense highs or deep lows, affecting the individual’s overall emotional state and functionality.
Diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder requires a thorough assessment by a mental health professional. The diagnostic criteria involve the presence of both psychotic and mood symptoms for a significant portion of time. To be diagnosed, the psychotic symptoms must occur without a major mood episode for at least two weeks, indicating that the psychosis is not solely a result of the mood disorder. Comprehensive evaluation includes clinical interviews, self-reports, and often input from family or close associates to understand the full scope and impact of the symptoms. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of the disorder.
3. Impact on Career Advancement
Schizoaffective disorder can have a profound impact on career advancement, affecting various aspects of professional life. Individuals with this condition may experience challenges with concentration, decision-making, and interpersonal interactions due to symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and mood fluctuations. These difficulties can hinder job performance and limit career opportunities.
The unpredictability of mood swings and psychotic episodes can also disrupt work schedules and affect productivity, potentially leading to frequent absences or inconsistent work quality. As a result, individuals might struggle with job stability and career progression. Additionally, the stigma associated with mental health conditions can create barriers, making it harder for individuals to advocate for their needs and pursue advancement opportunities.
Despite these challenges, many individuals with schizoaffective disorder find ways to succeed in their careers with appropriate support and accommodations. Open communication with employers and seeking workplace adjustments can help mitigate some of the impacts. Understanding and addressing these challenges are crucial for fostering a supportive work environment that allows individuals with schizoaffective disorder to thrive professionally.
4. Coping Strategies and Support
Effective coping strategies and support are essential for managing schizoaffective disorder and mitigating its impact on daily life. Developing a structured routine can help stabilize mood swings and manage symptoms, while maintaining regular medical appointments ensures ongoing evaluation and adjustment of treatment plans. Medication, typically including antipsychotics and mood stabilizers, plays a crucial role in symptom management.
Therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can assist individuals in coping with the psychotic and mood-related aspects of the disorder. Building a strong support network, including mental health professionals, family, and friends, provides emotional support and practical assistance.
Engaging in self-care practices, such as stress management techniques, exercise, and a healthy diet, also contributes to overall well-being. Additionally, joining support groups or online communities can offer valuable peer support and shared experiences. Implementing these strategies can significantly improve quality of life and help individuals navigate the challenges associated with schizoaffective disorder.
5. Workplace Accommodations
Workplace accommodations can play a vital role in supporting individuals with schizoaffective disorder, helping them manage their symptoms and enhance job performance. Adjustments tailored to individual needs can significantly improve work conditions and productivity.
Flexible work schedules allow employees to manage their symptoms more effectively, especially during periods of intense mood fluctuations or psychotic episodes. Part-time work or telecommuting options can provide a more stable environment and reduce stress.
Modifications to the work environment, such as a quieter workspace or noise-canceling headphones, can help minimize distractions and support concentration. Providing additional breaks or a quiet room for relaxation can also be beneficial during moments of overwhelming stress or fatigue.
Clear and consistent communication with supervisors about job expectations and feedback can help prevent misunderstandings and reduce anxiety. Additionally, employee assistance programs (EAPs) and access to mental health resources can offer ongoing support. Ensuring that workplace policies are inclusive and non-discriminatory fosters a supportive atmosphere, enabling employees with schizoaffective disorder to thrive and contribute effectively in their roles.
6. Personal Development and Self-Care
Personal development and self-care are crucial for individuals with schizoaffective disorder, as they help manage symptoms and enhance overall well-being. Establishing a consistent routine can provide structure and stability, which is beneficial for mood regulation and daily functioning. Setting realistic personal goals and breaking them into manageable tasks can boost self-esteem and provide a sense of accomplishment.
Self-care practices, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, contribute to overall mental and physical health. Incorporating relaxation techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress and improve emotional resilience. Engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy can also be therapeutic and provide a positive distraction from symptoms.
Building skills through self-study or personal development courses can enhance self-efficacy and open up new opportunities for growth. Emotional support from family, friends, or support groups provides validation and encouragement, while professional therapy offers strategies to cope with and understand the disorder better.
Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures that treatment plans are effective and adjusted as needed. By prioritizing self-care and personal development, individuals with schizoaffective disorder can improve their quality of life and achieve personal and professional goals.
7. Success Stories and Role Models
Success stories and role models provide inspiration and hope for individuals with schizoaffective disorder, demonstrating that it is possible to achieve personal and professional goals despite the challenges. Prominent figures such as John Nash, a Nobel Prize-winning mathematician, and the late artist and activist, Sylvia Plath, have publicly shared their experiences with mental health conditions, including schizoaffective disorder. Their stories highlight resilience and determination, illustrating how individuals can excel in their fields while managing their symptoms.
In addition to well-known figures, many people with schizoaffective disorder have made significant strides in various professions. Their achievements in fields such as writing, academia, and advocacy showcase their ability to overcome obstacles and contribute meaningfully to society. These role models often emphasize the importance of support systems, effective treatment, and self-care practices in their journeys. Sharing these success stories can provide valuable motivation and practical insights for others facing similar challenges, underscoring the potential for personal growth and career success despite the disorder.
8. Resources and Further Reading
For those seeking more information and support on schizoaffective disorder, numerous resources and further reading materials are available. The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) provides comprehensive information about schizoaffective disorder, including symptoms, treatment options, and research updates. The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) offers valuable resources, including support groups, educational materials, and advocacy programs that can help individuals and families navigate the challenges of the disorder.
Books such as “The Center Cannot Hold: My Journey Through Madness” by Elyn Saks offer personal insights into living with a severe mental illness, including schizoaffective disorder. Another recommended read is “The Noonday Demon: An Atlas of Depression” by Andrew Solomon, which explores the intersection of mental health conditions and personal experiences.
Online platforms like the Schizophrenia and Related Disorders Alliance of America (SARDAA) and Mental Health America (MHA) provide further resources, including forums, articles, and helplines. These resources are essential for gaining a deeper understanding of schizoaffective disorder, accessing support networks, and finding strategies for effective management and personal development.
Understanding schizoaffective disorder and its impacts on career advancement and personal development is crucial for effective management and personal growth. By exploring symptoms, coping strategies, and workplace accommodations, individuals can navigate the challenges more effectively. Success stories and available resources offer hope and guidance, empowering those affected to pursue their goals and lead fulfilling lives.
terylblog.com